以下分析基于Android S.
简述 本文集中研究input和窗口的关系, 特别是input系统是如何将事件传给正确的窗口进程的。
在Activity的resume过程中,会通过ViewRootImpl.setView向WMS传递其窗口信息,我们还是从这里入手:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public void setView (View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView, int userId) { ...... requestLayout(); InputChannel inputChannel = null ; if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures & WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0 ) { inputChannel = new InputChannel (); } ....... res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mWindowAttributes, getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId, mInsetsController.getRequestedVisibility(), inputChannel, mTempInsets, mTempControls); ...... if (inputChannel != null ) { ...... mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver (inputChannel, Looper.myLooper()); ...... } ...... } public int addWindow (Session session, IWindow client, LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId, int requestUserId, InsetsState requestedVisibility, InputChannel outInputChannel, InsetsState outInsetsState, InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls) { ...... final WindowState win = new WindowState (this , session, client, token, parentWindow, appOp[0 ], attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid, userId, session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow); ...... final boolean openInputChannels = (outInputChannel != null && (attrs.inputFeatures & INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0 ); if (openInputChannels) { win.openInputChannel(outInputChannel); } ...... }
注意初始化InputChannel是在WindowState之后,也是通过其openInputChannel的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 void openInputChannel (InputChannel outInputChannel) { if (mInputChannel != null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("Window already has an input channel." ); } String name = getName(); mInputChannel = mWmService.mInputManager.createInputChannel(name); mInputChannelToken = mInputChannel.getToken(); mInputWindowHandle.setToken(mInputChannelToken); mWmService.mInputToWindowMap.put(mInputChannelToken, this ); if (outInputChannel != null ) { mInputChannel.copyTo(outInputChannel); } else { mDeadWindowEventReceiver = new DeadWindowEventReceiver (mInputChannel); } }
1 2 3 4 5 private static native InputChannel nativeCreateInputChannel (long ptr, String name) ;public InputChannel createInputChannel (String name) { return nativeCreateInputChannel(mPtr, name); }
通过JNI由native层创建InputChannel。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 static jobject nativeCreateInputChannel (JNIEnv* env, jclass , jlong ptr, jstring nameObj) NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast <NativeInputManager*>(ptr); ScopedUtfChars nameChars (env, nameObj) ; std::string name = nameChars.c_str (); base::Result<std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>> inputChannel = im->createInputChannel (env, name); if (!inputChannel.ok ()) { std::string message = inputChannel.error ().message (); message += StringPrintf (" Status=%d" , inputChannel.error ().code ()); jniThrowRuntimeException (env, message.c_str ()); return nullptr ; } jobject inputChannelObj = android_view_InputChannel_createJavaObject (env, std::move (*inputChannel)); if (!inputChannelObj) { return nullptr ; } android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback (env, inputChannelObj, handleInputChannelDisposed, im); return inputChannelObj; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 base::Result<std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>> NativeInputManager::createInputChannel ( JNIEnv* , const std::string& name) { ATRACE_CALL (); return mInputManager->getDispatcher ()->createInputChannel (name); } sp<InputDispatcherInterface> InputManager::getDispatcher () { return mDispatcher; }
关于InputDispatcher的初始化后续单独分析。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 Result<std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>> InputDispatcher::createInputChannel (const std::string& name) { std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> serverChannel; std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> clientChannel; status_t result = InputChannel::openInputChannelPair (name, serverChannel, clientChannel); if (result) { return base::Error (result) << "Failed to open input channel pair with name " << name; } { std::scoped_lock _l(mLock); const sp<IBinder>& token = serverChannel->getConnectionToken (); int fd = serverChannel->getFd (); sp<Connection> connection = new Connection (std::move (serverChannel), false , mIdGenerator); if (mConnectionsByToken.find (token) != mConnectionsByToken.end ()) { ALOGE ("Created a new connection, but the token %p is already known" , token.get ()); } mConnectionsByToken.emplace (token, connection); std::function<int (int events)> callback = std::bind (&InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback, this , std::placeholders::_1, token); mLooper->addFd (fd, 0 , ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, new LooperEventCallback (callback), nullptr ); } mLooper->wake (); return clientChannel; }
创建Native层的InputChannel其实就是利用socket创建了一对套接字,分别作为服务端和客户端,并将服务端的token作为key,存入作为记录此次InputChannel的Connection至mConnectionsByToken中。其后利用bind绑定handleReceiveCallback作为回调函数(注意这里固定了其第二个参数为当前的token),然后将服务端的文件描述符存入mLooper中。最后唤醒mLooper。
注意这里的mLooper是InputDispatcher初始化时创建的:
mLooper = new Looper(false);
所以这里InputChannel中的服务端就是用来分发input事件的,而客户端的InputChannel应该就需要传给对应的应用进程了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 status_t InputChannel::openInputChannelPair (const std::string& name, std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>& outServerChannel, std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>& outClientChannel) int sockets[2 ]; if (socketpair (AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET, 0 , sockets)) { status_t result = -errno; ALOGE ("channel '%s' ~ Could not create socket pair. errno=%s(%d)" , name.c_str (), strerror (errno), errno); outServerChannel.reset (); outClientChannel.reset (); return result; } int bufferSize = SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE; setsockopt (sockets[0 ], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof (bufferSize)); setsockopt (sockets[0 ], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof (bufferSize)); setsockopt (sockets[1 ], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof (bufferSize)); setsockopt (sockets[1 ], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof (bufferSize)); sp<IBinder> token = new BBinder (); std::string serverChannelName = name + " (server)" ; android::base::unique_fd serverFd (sockets[0 ]) ; outServerChannel = InputChannel::create (serverChannelName, std::move (serverFd), token); std::string clientChannelName = name + " (client)" ; android::base::unique_fd clientFd (sockets[1 ]) ; outClientChannel = InputChannel::create (clientChannelName, std::move (clientFd), token); return OK; }
socketpair()函数用于创建一对无名的、相互连接的套接字。如果函数成功,则返回0,创建好的套接字分别是sockets[0]和sockets[1];否则返回-1,错误码保存于errno中。
这对套接字可以用于全双工通信,每一个套接字既可以读也可以写。例如,可以往sockets[0]中写,从sockets[1]中读;或者从sockets[1]中写,从sockets[0]中读;
如果往一个套接字(如sockets[0])中写入后,再从该套接字读时会阻塞,只能在另一个套接字中(sockets[1])上读成功;
读、写操作可以位于同一个进程,也可以分别位于不同的进程。因为sockets[0]和sockets[1]是进程共享的,所以读的进程要关闭写描述符, 反之,写的进程关闭读描述符。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> InputChannel::create (const std::string& name, android::base::unique_fd fd, sp<IBinder> token) const int result = fcntl (fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK); if (result != 0 ) { LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL ("channel '%s' ~ Could not make socket non-blocking: %s" , name.c_str (), strerror (errno)); return nullptr ; } return std::unique_ptr <InputChannel>(new InputChannel (name, std::move (fd), token)); } InputChannel::InputChannel (const std::string name, android::base::unique_fd fd, sp<IBinder> token) : mName (std::move (name)), mFd (std::move (fd)), mToken (std::move (token)) { if (DEBUG_CHANNEL_LIFECYCLE) { ALOGD ("Input channel constructed: name='%s', fd=%d" , getName ().c_str (), getFd ().get ()); } }
native层的InputChannel原来就是一对套接字,分成server端和client端,用于跨进程通信。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 jobject android_view_InputChannel_createJavaObject (JNIEnv* env, std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> inputChannel) std::string name = inputChannel->getName (); jlong ptr = android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel (env, std::move (inputChannel)); jobject javaInputChannel = env->NewObject (gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz, gInputChannelClassInfo.mCtor); if (!javaInputChannel) { ALOGE ("Failed to create a Java InputChannel for channel %s." , name.c_str ()); return nullptr ; } env->CallVoidMethod (javaInputChannel, gInputChannelClassInfo.mSetNativeInputChannel, ptr); if (env->ExceptionOccurred ()) { ALOGE ("Failed to set native ptr to the Java InputChannel for channel %s." , inputChannel->getName ().c_str ()); return nullptr ; } return javaInputChannel; } static jlong android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel ( JNIEnv* env, std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> inputChannel) std::unique_ptr<NativeInputChannel> nativeInputChannel = std::make_unique <NativeInputChannel>(std::move (inputChannel)); return reinterpret_cast <jlong>(nativeInputChannel.release ()); } NativeInputChannel::NativeInputChannel (std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> inputChannel) : mInputChannel (std::move (inputChannel)), mDisposeCallback (nullptr ) {}
经过1.3 我们知道这里传入的InputChannel其实是一对socket中代表客户端的那个, 先通过std::move将InputChannel存入新创建的NativeInputChannel对象中,然后通过JNI构造出java层的InputChannel,在调用其setNativeInputChannel,将NativeInputChannel保存在其mPtr中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 private void setNativeInputChannel (long nativeChannel) { if (nativeChannel == 0 ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Attempting to set native input channel to null." ); } if (mPtr != 0 ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Already has native input channel." ); } if (DEBUG) { Slog.d(TAG, "setNativeInputChannel : " + String.format("%x" , nativeChannel)); } sRegistry.registerNativeAllocation(this , nativeChannel); mPtr = nativeChannel; }
所以java层的InputChannel里的mPtr是对应NativeInputChannel对象的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 void android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback (JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj, InputChannelObjDisposeCallback callback, void * data) NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel (env, inputChannelObj); if (!nativeInputChannel || !nativeInputChannel->getInputChannel ()) { ALOGW ("Cannot set dispose callback because input channel object has not been initialized." ); } else { nativeInputChannel->setDisposeCallback (callback, data); } } static NativeInputChannel* android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel (JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj) jlong longPtr = env->GetLongField (inputChannelObj, gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr); return reinterpret_cast <NativeInputChannel*>(longPtr); }
1 2 3 4 void NativeInputChannel::setDisposeCallback (InputChannelObjDisposeCallback callback, void * data) mDisposeCallback = callback; mDisposeData = data; }
将回调函数和相关参数保存起来, 当进程死亡,或者窗口被销毁时,会主动调用InputChannel.dispose()回收资源,最后就会调用到NativeInputChannel.dispose了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 void NativeInputChannel::dispose (JNIEnv* env, jobject obj) if (!mInputChannel) { return ; } if (mDisposeCallback) { mDisposeCallback (env, obj, mInputChannel, mDisposeData); mDisposeCallback = nullptr ; mDisposeData = nullptr ; } mInputChannel.reset (); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 static void handleInputChannelDisposed (JNIEnv* env, jobject , const std::shared_ptr<InputChannel>& inputChannel, void * data) NativeInputManager* im = static_cast <NativeInputManager*>(data); ALOGW ("Input channel object '%s' was disposed without first being removed with " "the input manager!" , inputChannel->getName ().c_str ()); im->removeInputChannel (env, inputChannel->getConnectionToken ()); } status_t NativeInputManager::removeInputChannel (JNIEnv* , const sp<IBinder>& connectionToken) ATRACE_CALL (); return mInputManager->getDispatcher ()->removeInputChannel (connectionToken); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 status_t InputDispatcher::removeInputChannel (const sp<IBinder>& connectionToken) { std::scoped_lock _l(mLock); status_t status = removeInputChannelLocked (connectionToken, false ); if (status) { return status; } } mLooper->wake (); return OK; } status_t InputDispatcher::removeInputChannelLocked (const sp<IBinder>& connectionToken, bool notify) sp<Connection> connection = getConnectionLocked (connectionToken); if (connection == nullptr ) { return BAD_VALUE; } removeConnectionLocked (connection); if (connection->monitor) { removeMonitorChannelLocked (connectionToken); } mLooper->removeFd (connection->inputChannel->getFd ()); nsecs_t currentTime = now (); abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked (currentTime, connection, notify); connection->status = Connection::STATUS_ZOMBIE; return OK; }
移除InputChannel的工作也不多,将Connection从直接保存的集合中移除,顺便将其中保存的服务端Socket描述符从mLooper中移除即可。最后标记被移除的Connection状态为ZOMBIE状态。
1 2 3 4 5 void InputDispatcher::removeConnectionLocked (const sp<Connection>& connection) mAnrTracker.eraseToken (connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken ()); mConnectionsByToken.erase (connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken ()); }
直接将该Connection从mConnectionsByToken和mAnrTracker中移除即可。
通过 InputChannel的初始化 我们知道InputChannel的Native实现就是一对Socket,其中服务端作为input事件分发者被加入InputDispatcher的Looper中,客户端会被存入NativeInputChannel中,而后通过JNI存入java层的InputChannel的mPtr中,但是这里java层的InputChannel还是处于SystemServer进程,还没有看到应用进程InputChannel是如何被赋值的。
接下来我们先研究下InputChannel的拷贝。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void copyTo (InputChannel outParameter) { if (outParameter == null ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("outParameter must not be null" ); } if (outParameter.mPtr != 0 ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Other object already has a native input channel." ); } outParameter.setNativeInputChannel(nativeDup(mPtr)); } private native long nativeDup (long channel) ;
这里思考一下为什么不直接将mPtr赋值给outParameter的mPtr呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 static jlong android_view_InputChannel_nativeDup (JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jlong channel) NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel = reinterpret_cast <NativeInputChannel*>(channel); if (nativeInputChannel == nullptr ) { jniThrowRuntimeException (env, "InputChannel has no valid NativeInputChannel" ); return 0 ; } std::shared_ptr<InputChannel> inputChannel = nativeInputChannel->getInputChannel (); if (inputChannel == nullptr ) { jniThrowRuntimeException (env, "NativeInputChannel has no corresponding InputChannel" ); return 0 ; } std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> dupInputChannel = inputChannel->dup (); if (dupInputChannel == nullptr ) { std::string message = android::base::StringPrintf ( "Could not duplicate input channel %s" , inputChannel->getName ().c_str ()); jniThrowRuntimeException (env, message.c_str ()); } return reinterpret_cast <jlong>(new NativeInputChannel (std::move (dupInputChannel))); }
android_view_InputChannel_nativeDup的作用就是根据传入的java层InputChannel创建一个新的NativeInputChannel作为客户端socket, 与服务端Socket的InputChannel对应。
1 2 3 4 5 6 std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> InputChannel::dup () const { base::unique_fd newFd (dupFd()) ; return InputChannel::create (getName (), std::move (newFd), getConnectionToken ()); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 base::unique_fd InputChannel::dupFd () const { android::base::unique_fd newFd (::dup(getFd())) ; if (!newFd.ok ()) { ALOGE ("Could not duplicate fd %i for channel %s: %s" , getFd ().get (), getName ().c_str (), strerror (errno)); const bool hitFdLimit = errno == EMFILE || errno == ENFILE; LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF (hitFdLimit, "Too many open files, could not duplicate input channel %s" , getName ().c_str ()); return {}; } return newFd; }
dupFd是通过 ::dup(int oldFd) 函数复制文件描述符,使新的文件描述符指向参数描述符指向的同一个文件。
2.4 Binder通信中AIDL里的out标记 看完了InputChannel的copyTo函数,我们知道该函数就是在native层创建了新的NativeInputChannel,但是还是和之前客户端InputChannel一样指向同一个Socket描述符,这样服务端Socket发的消息会同步传给信息的InputChannel了。
但是这里我们还是没有看到应用进程的InputChannel是如何被赋值的,在WMS.addWindow函数中,outInputChannel在被mInputChannel.copyTo函数赋值后,就没有继续使用过了。这里我们就要看到应用进程和WMS通信的桥梁Session的AIDL文件定义了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 int addToDisplay (IWindow window, in WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, in int viewVisibility, in int layerStackId, in InsetsState requestedVisibility, out InputChannel outInputChannel, out InsetsState insetsState, out InsetsSourceControl[] activeControls) ;int addToDisplayAsUser (IWindow window, in WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, in int viewVisibility, in int layerStackId, in int userId, in InsetsState requestedVisibility, out InputChannel outInputChannel, out InsetsState insetsState, out InsetsSourceControl[] activeControls) ;int addToDisplayWithoutInputChannel (IWindow window, in WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, in int viewVisibility, in int layerStackId, out InsetsState insetsState) ;
毫无意外,所有的InputChannel都是被标记了out标签,这样binder回调时会将该参数回传给调用进程,即应用进程。 这样一来一个WindowState对应一对Socket,分成服务端和客户端,服务端Socket的描述符被存入InputDispatcher的mConnectionsByToken,也被添加到其mLooper中用于转发Input事件至客户端Socket中。而客户端Socket又被dup函数复制成两份NativeInputChannel, 一份存在WindowState的mInputChannel中,另一份通过Binder调用存入应用进程的ViewRootImpl的WindowInputEventReceiver对象中。
在ViewRootImpl.setView函数中,当应用进程通过binder调用addToDisplayAsUser获得被复制的InputChannel后,会通过该InputChannel创建WindowInputEventReceiver。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver { public WindowInputEventReceiver (InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) { super (inputChannel, looper); } ...... }
WindowInputEventReceiver是继承了InputEventReceiver的,这里的构造函数也仅仅是将传入的参数继续调用给父类的构造函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public InputEventReceiver (InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) { if (inputChannel == null ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("inputChannel must not be null" ); } if (looper == null ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("looper must not be null" ); } mInputChannel = inputChannel; mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue(); mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference <InputEventReceiver>(this ), inputChannel, mMessageQueue); mCloseGuard.open("dispose" ); } private static native long nativeInit (WeakReference<InputEventReceiver> receiver, InputChannel inputChannel, MessageQueue messageQueue) ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 static jlong nativeInit (JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject receiverWeak, jobject inputChannelObj, jobject messageQueueObj) std::shared_ptr<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel (env, inputChannelObj); if (inputChannel == nullptr ) { jniThrowRuntimeException (env, "InputChannel is not initialized." ); return 0 ; } sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue (env, messageQueueObj); if (messageQueue == nullptr ) { jniThrowRuntimeException (env, "MessageQueue is not initialized." ); return 0 ; } sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = new NativeInputEventReceiver (env, receiverWeak, inputChannel, messageQueue); status_t status = receiver->initialize (); if (status) { std::string message = android::base::StringPrintf ("Failed to initialize input event receiver. status=%d" , status); jniThrowRuntimeException (env, message.c_str ()); return 0 ; } receiver->incStrong (gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.clazz); return reinterpret_cast <jlong>(receiver.get ()); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 NativeInputEventReceiver::NativeInputEventReceiver ( JNIEnv* env, jobject receiverWeak, const std::shared_ptr<InputChannel>& inputChannel, const sp<MessageQueue>& messageQueue) : mReceiverWeakGlobal (env->NewGlobalRef (receiverWeak)), mInputConsumer (inputChannel), mMessageQueue (messageQueue), mBatchedInputEventPending (false ), mFdEvents (0 ) { if (kDebugDispatchCycle) { ALOGD ("channel '%s' ~ Initializing input event receiver." , getInputChannelName ().c_str ()); } }
初始化NativeInputEventReceiver
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::initialize () setFdEvents (ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT); return OK; } void NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents (int events) if (mFdEvents != events) { mFdEvents = events; int fd = mInputConsumer.getChannel ()->getFd (); if (events) { mMessageQueue->getLooper ()->addFd (fd, 0 , events, this , nullptr ); } else { mMessageQueue->getLooper ()->removeFd (fd); } } }
这里设置文件描述符,将作为客户端InputChannel的Socket的描述符添加到该应用进程的主线程Looper中(ViewRootImpl.setView是主线程才能被调用的)。
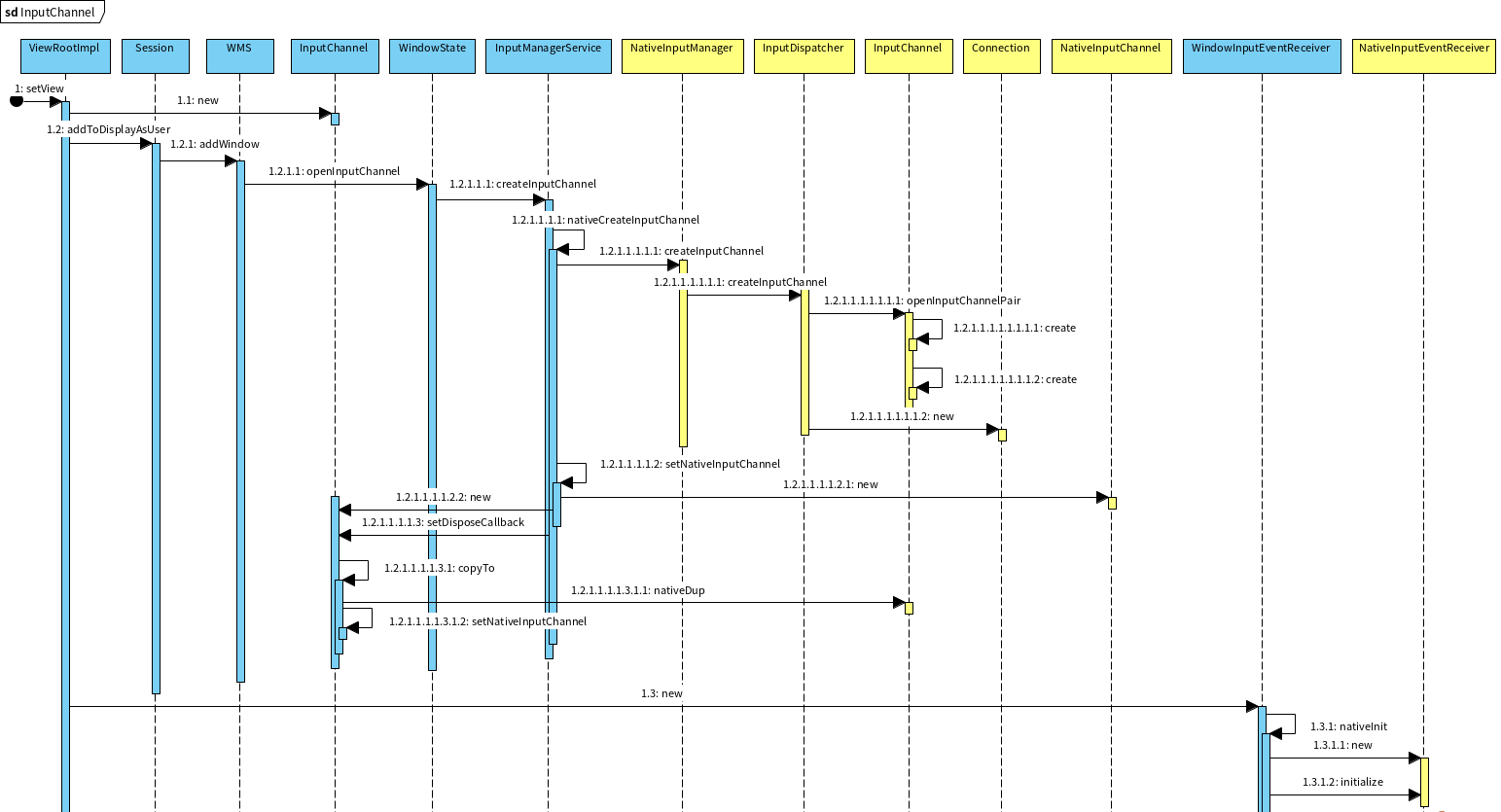
四. 小结 WindowState和InputChannel的相关流程图如下:
InputChannel的Native实现就是一对Socket,其中服务端作为input事件分发者被加入InputDispatcher的Looper中,客户端会被存入NativeInputChannel中。一个WindowState对应一对Socket,分成服务端和客户端,服务端Socket的描述符被存入InputDispatcher的mConnectionsByToken,也被添加到其mLooper中用于转发Input事件至客户端Socket中。而客户端Socket又被dup函数复制成两份NativeInputChannel, 一份存在WindowState的mInputChannel中,另一份通过Binder调用存入应用进程的ViewRootImpl的WindowInputEventReceiver对象中。
接下来我们看看input事件是如何传给正确的窗口进程的。