以下分析基于Android S.
简述 这篇文章中我们重点关注焦点窗口的更新,所谓焦点窗口就是当前选择的窗口。在Android里可以通过下面的adb命令来查看当前的焦点窗口:
adb shell dumpsys window |grep -iE “mCurr*”
我们知道一个实体显示器对应一个DisplayId, 相应的有一个DisplayContent,如同我们人眼或者相机的对焦,同一时刻只能有一个焦点,那么对应一个Display一般来说也只有一个焦点窗口了。
我们之前一直分析的WMS.addWindow,在应用进程调用setView传入对应窗口属性之后,当然也会有焦点窗口的重新计算了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public int addWindow (Session session, IWindow client, LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId, int requestUserId, InsetsState requestedVisibility, InputChannel outInputChannel, InsetsState outInsetsState, InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls) { ...... final int type = attrs.type; synchronized (mGlobalLock) { ...... WindowToken token = displayContent.getWindowToken( hasParent ? parentWindow.mAttrs.token : attrs.token); ... final WindowState win = new WindowState (this , session, client, token, parentWindow, appOp[0 ], attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid, userId, session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow); ...... win.attach(); mWindowMap.put(client.asBinder(), win); win.initAppOpsState(); ...... win.mToken.addWindow(win); ...... boolean focusChanged = false ; if (win.canReceiveKeys()) { focusChanged = updateFocusedWindowLocked(UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS, false ); if (focusChanged) { imMayMove = false ; } } ...... if (focusChanged) { displayContent.getInputMonitor().setInputFocusLw(displayContent.mCurrentFocus, false ); } ...... if (win.isVisibleOrAdding() && displayContent.updateOrientation()) { displayContent.sendNewConfiguration(); } ...... }
一. 焦点窗口更新 应用的第一个addWindow应该是启动窗口的,所以我们以启动窗口为例分析焦点窗口更新。
1.1 WindowState.canReceiveKeys 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 boolean canReceiveKeys () { return canReceiveKeys(false ); } public boolean canReceiveKeys (boolean fromUserTouch) { final boolean canReceiveKeys = isVisibleOrAdding() && (mViewVisibility == View.VISIBLE) && !mRemoveOnExit && ((mAttrs.flags & WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE) == 0 ) && (mActivityRecord == null || mActivityRecord.windowsAreFocusable(fromUserTouch)) && canReceiveTouchInput(); if (!canReceiveKeys) { return false ; } return fromUserTouch || getDisplayContent().isOnTop() || getDisplayContent().isTrusted(); }
这里检查了一堆参数,我们一一分析:
isVisibleOrAdding(): 判断当前窗口是否可见或者被添加
mViewVisibility == View.VISIBLE: 窗口可见属性为VISIBLE
!mRemoveOnExit: 该窗口没有移除或者退出
((mAttrs.flags & WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE) == 0): 该窗口的属性不带有FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE,是可聚焦的
(mActivityRecord == null || mActivityRecord.windowsAreFocusable(fromUserTouch)):该窗口不是Activity对应的窗口,如果是那么需要满足windowsAreFocusable
canReceiveTouchInput(): 该窗口可以接收touch事件
只有当上述条件都满足且窗口所处的DisplayContent是最上层的并且该Display是受信任的,该窗口才可能接收事件。
1.1.1 WindowState.isVisibleOrAdding 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 boolean isVisibleOrAdding () { final ActivityRecord atoken = mActivityRecord; return (mHasSurface || (!mRelayoutCalled && mViewVisibility == View.VISIBLE)) && isVisibleByPolicy() && !isParentWindowHidden() && (atoken == null || atoken.mVisibleRequested) && !mAnimatingExit && !mDestroying; } boolean isVisibleByPolicy () { return (mPolicyVisibility & POLICY_VISIBILITY_ALL) == POLICY_VISIBILITY_ALL; } boolean isParentWindowHidden () { final WindowState parent = getParentWindow(); return parent != null && parent.mHidden; }
判断该窗口是否可见或者处于被添加状态。
(mHasSurface || (!mRelayoutCalled && mViewVisibility == View.VISIBLE)):
mHasSurface:该窗口是否有对应Surface,该Surface会在该窗口对应的启动或退出动画时创建
(!mRelayoutCalled && mViewVisibility == View.VISIBLE):
!mRelayoutCalled: 该窗口被调用了relayoutWindow
mViewVisibility == View.VISIBLE: 窗口View属性对应的是VISIBLE
如果该窗口已经有Surface或者没有被relayoutWindow但窗口可见属性是VISIBLE的时
isVisibleByPolicy():判断mPolicyVisibility中的POLICY_VISIBILITY_ALL位都被设置了
!isParentWindowHidden(): 判断父窗口没有被隐藏
(atoken == null || atoken.mVisibleRequested):
atoken == null:该窗口不对应ActivityRecord
atoken.mVisibleRequested: 如果对应,需要mVisibleRequested被设置为true
!mAnimatingExit:该窗口当前没有执行退出动画
!mDestroying:该窗口没有被销毁
1.1.2 ActivityRecord.windowsAreFocusable 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 boolean windowsAreFocusable (boolean fromUserTouch) { if (!fromUserTouch && mTargetSdk < Build.VERSION_CODES.Q) { final int pid = getPid(); final ActivityRecord topFocusedAppOfMyProcess = mWmService.mRoot.mTopFocusedAppByProcess.get(pid); if (topFocusedAppOfMyProcess != null && topFocusedAppOfMyProcess != this ) { return false ; } } return (canReceiveKeys() || isAlwaysFocusable()) && isAttached(); } boolean canReceiveKeys () { return getWindowConfiguration().canReceiveKeys() && (task == null || task.getWindowConfiguration().canReceiveKeys()); } private boolean isAlwaysFocusable () { return (info.flags & FLAG_ALWAYS_FOCUSABLE) != 0 ; }
windowsAreFocusable用于判断该ActivityRecord对应窗口是否可以接收input事件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 boolean canReceiveTouchInput () { if (mActivityRecord == null || mActivityRecord.getTask() == null ) { return true ; } return !mActivityRecord.getTask().getRootTask().shouldIgnoreInput() && mActivityRecord.mVisibleRequested && !isRecentsAnimationConsumingAppInput(); }
这里可以看到如果是非ActivityRecord对应的Window那么直接返回true,如果该ActivityRecord还没有被加入task也直接返回true.
!mActivityRecord.getTask().getRootTask().shouldIgnoreInput():该ActivityRecord的task所处的rootTask没有被设置忽略input事件
mActivityRecord.mVisibleRequested: 该ActivityRecord被设置了VISIBLE
!isRecentsAnimationConsumingAppInput():该窗口没有作为最近任务窗口的动画的一部分时
1.2 WMS.updateFocusedWindowLocked 1 2 3 4 5 6 boolean updateFocusedWindowLocked (int mode, boolean updateInputWindows) { Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "wmUpdateFocus" ); boolean changed = mRoot.updateFocusedWindowLocked(mode, updateInputWindows); Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER); return changed; }
这里传入的mode是UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS,而且updateInputWindows为false. WMS.mRoot就是RootWindowContainer.
1.3 RootWindowContainer.updateFocusedWindowLocked 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 boolean updateFocusedWindowLocked (int mode, boolean updateInputWindows) { mTopFocusedAppByProcess.clear(); boolean changed = false ; int topFocusedDisplayId = INVALID_DISPLAY; for (int i = mChildren.size() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; --i) { final DisplayContent dc = mChildren.get(i); changed |= dc.updateFocusedWindowLocked(mode, updateInputWindows, topFocusedDisplayId); final WindowState newFocus = dc.mCurrentFocus; if (newFocus != null ) { final int pidOfNewFocus = newFocus.mSession.mPid; if (mTopFocusedAppByProcess.get(pidOfNewFocus) == null ) { mTopFocusedAppByProcess.put(pidOfNewFocus, newFocus.mActivityRecord); } if (topFocusedDisplayId == INVALID_DISPLAY) { topFocusedDisplayId = dc.getDisplayId(); } } else if (topFocusedDisplayId == INVALID_DISPLAY && dc.mFocusedApp != null ) { topFocusedDisplayId = dc.getDisplayId(); } } if (topFocusedDisplayId == INVALID_DISPLAY) { topFocusedDisplayId = DEFAULT_DISPLAY; } if (mTopFocusedDisplayId != topFocusedDisplayId) { mTopFocusedDisplayId = topFocusedDisplayId; mWmService.mInputManager.setFocusedDisplay(topFocusedDisplayId); mWmService.mPolicy.setTopFocusedDisplay(topFocusedDisplayId); ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_FOCUS_LIGHT, "New topFocusedDisplayId=%d" , topFocusedDisplayId); } return changed; }
计算更新焦点窗口是对所有DisplayContent的依次计算更新焦点窗口。首先清除mTopFocusedAppByProcess中的元素,然后依次更新所有DisplayContent的焦点窗口。
1.4 DisplayContent.updateFocusedWindowLocked 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 boolean updateFocusedWindowLocked (int mode, boolean updateInputWindows, int topFocusedDisplayId) { WindowState newFocus = findFocusedWindowIfNeeded(topFocusedDisplayId); if (mCurrentFocus == newFocus) { return false ; } boolean imWindowChanged = false ; final WindowState imWindow = mInputMethodWindow; if (imWindow != null ) { ...... } ProtoLog.d(WM_DEBUG_FOCUS_LIGHT, "Changing focus from %s to %s displayId=%d Callers=%s" , mCurrentFocus, newFocus, getDisplayId(), Debug.getCallers(4 )); final WindowState oldFocus = mCurrentFocus; mCurrentFocus = newFocus; if (newFocus != null ) { mWinAddedSinceNullFocus.clear(); mWinRemovedSinceNullFocus.clear(); if (newFocus.canReceiveKeys()) { newFocus.mToken.paused = false ; } } onWindowFocusChanged(oldFocus, newFocus); int focusChanged = getDisplayPolicy().focusChangedLw(oldFocus, newFocus); ...... if ((focusChanged & FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_LAYOUT) != 0 ) { setLayoutNeeded(); if (mode == UPDATE_FOCUS_PLACING_SURFACES) { performLayout(true , updateInputWindows); } else if (mode == UPDATE_FOCUS_REMOVING_FOCUS) { mWmService.mRoot.performSurfacePlacement(); } } ...... scheduleToastWindowsTimeoutIfNeededLocked(oldFocus, newFocus); ...... mLastFocus = mCurrentFocus; return true ; }
DisplayContent更新焦点窗口的流程如下:
计算当前DisplayContent的焦点窗口
如果计算的新焦点窗口和当前焦点窗口是同一个,则无需额外动作
如果当前存在输入法窗口,执行相关操作(后续分析输入法窗口)
更新焦点窗口,保存在mCurrentFocus中
清空mWinAddedSinceNullFocus、mWinRemovedSinceNullFocus
通知其他模组焦点窗口更新了,主要是更新两个Task(当前焦点窗口和新的焦点窗口所处的Task)的阴影
更新DisplayPolicy中相关参数
更新DisplayFoldController中的mFocusedApp(焦点窗口包名),然后根据需要更新SystemUI的可见性
如果因焦点窗口变化导致SystemUI状态栏或者导航栏可见性有变化了,将参数mLayoutNeeded置位true
将没有焦点的窗口的toast在超时时间后移除,防止其覆盖UI
记录新焦点窗口,保存在mLastFocus中
1.4.1 DisplayContent.findFocusedWindowIfNeeded 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 WindowState findFocusedWindowIfNeeded (int topFocusedDisplayId) { return (mWmService.mPerDisplayFocusEnabled || topFocusedDisplayId == INVALID_DISPLAY) ? findFocusedWindow() : null ; } WindowState findFocusedWindow () { mTmpWindow = null ; forAllWindows(mFindFocusedWindow, true ); if (mTmpWindow == null ) { ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_FOCUS_LIGHT, "findFocusedWindow: No focusable windows, display=%d" , getDisplayId()); return null ; } return mTmpWindow; }
注意这里的mFindFocusedWindow其实是一个函数: ToBooleanFunction mFindFocusedWindow, 这里又是使用了函数式编程的方法。我们先看forAllWindows方法,这个是被继承的祖父类WindowContainer中的方法。
1.4.1.1 WindowContainer.forAllWindows 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 boolean forAllWindows (ToBooleanFunction<WindowState> callback, boolean traverseTopToBottom) { if (traverseTopToBottom) { for (int i = mChildren.size() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; --i) { if (mChildren.get(i).forAllWindows(callback, traverseTopToBottom)) { return true ; } } } else { final int count = mChildren.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) { if (mChildren.get(i).forAllWindows(callback, traverseTopToBottom)) { return true ; } } } return false ; }
对该WindowContainer的mChildren中的每一个元素执行forAllWindows,调用callback。traverseTopToBottom参数如果为true,则按z顺序从上到下遍历层次结构,否则从下到上遍历。如果因为传入的函数callback执行后的返回值为true,那么会中止遍历直接返回true。
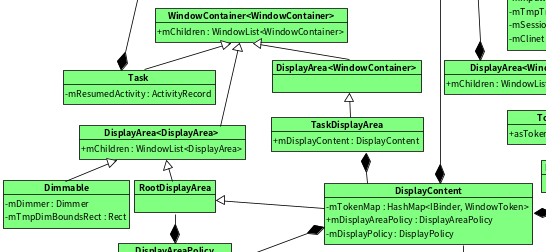
回顾下DisplayContent的类图:
可以看到DisplayContent的是从WindowContainer一路继承下来的,所以其mChildren就是 WindowList。
而DisplayArea也是继承了WindowContainer,所以到底这个DisplayContent里存储了什么元素呢? 回到之前我们研究过的DisplayContent的创建 WMS(2)-WMS中RootDisplayArea的创建
1.4.1.2 WindowState.forAllWindows 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Override boolean forAllWindows (ToBooleanFunction<WindowState> callback, boolean traverseTopToBottom) { if (mChildren.isEmpty()) { return applyInOrderWithImeWindows(callback, traverseTopToBottom); } if (traverseTopToBottom) { return forAllWindowTopToBottom(callback); } else { return forAllWindowBottomToTop(callback); } }
这里我们假设该mChildren为null:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 private boolean applyInOrderWithImeWindows (ToBooleanFunction<WindowState> callback, boolean traverseTopToBottom) { if (traverseTopToBottom) { if (applyImeWindowsIfNeeded(callback, traverseTopToBottom) || callback.apply(this )) { return true ; } } else { if (callback.apply(this ) || applyImeWindowsIfNeeded(callback, traverseTopToBottom)) { return true ; } } return false ; }
1.4.2 DisplayContent.onWindowFocusChanged 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private static void onWindowFocusChanged (WindowState oldFocus, WindowState newFocus) { final Task focusedTask = newFocus != null ? newFocus.getTask() : null ; final Task unfocusedTask = oldFocus != null ? oldFocus.getTask() : null ; if (focusedTask == unfocusedTask) { return ; } if (focusedTask != null ) { focusedTask.onWindowFocusChanged(true ); } if (unfocusedTask != null ) { unfocusedTask.onWindowFocusChanged(false ); } }
从WindowState中拿到的Task其实是其对应的ActivityRecord所在的Task:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Task getTask () { return mActivityRecord != null ? mActivityRecord.getTask() : null ; } Task getTask () { return task; }
这个ActivityRecord.task就是 WMS(3)-ActivityRecord和WindowToken
1.4.2.1 Task.onWindowFocusChanged 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void onWindowFocusChanged (boolean hasFocus) { updateShadowsRadius(hasFocus, getSyncTransaction()); } private void updateShadowsRadius (boolean taskIsFocused, SurfaceControl.Transaction pendingTransaction) { if (!mWmService.mRenderShadowsInCompositor || !isRootTask()) return ; final float newShadowRadius = getShadowRadius(taskIsFocused); if (mShadowRadius != newShadowRadius) { mShadowRadius = newShadowRadius; pendingTransaction.setShadowRadius(getSurfaceControl(), mShadowRadius); } }
这里根据该task是否持有焦点来更新阴影,后续研究
1.4.3 DisplayPolicy.focusChangedLw 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public int focusChangedLw (WindowState lastFocus, WindowState newFocus) { mFocusedWindow = newFocus; mLastFocusedWindow = lastFocus; if (mDisplayContent.isDefaultDisplay) { mService.mPolicy.onDefaultDisplayFocusChangedLw(newFocus); } if (updateSystemUiVisibilityLw()) { return FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_LAYOUT; } return 0 ; }
这里更新DisplayPolicy中存储的焦点窗口相关信息,包括更新DisplayFoldController中的mFocusedApp(焦点窗口包名),然后根据需要更新SystemUI的可见性。
1.5 DisplayContent.mFindFocusedWindow 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 private final ToBooleanFunction<WindowState> mFindFocusedWindow = w -> { final ActivityRecord focusedApp = mFocusedApp; ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_FOCUS, "Looking for focus: %s, flags=%d, canReceive=%b, reason=%s" , w, w.mAttrs.flags, w.canReceiveKeys(), w.canReceiveKeysReason(false )); if (!w.canReceiveKeys()) { return false ; } final ActivityRecord activity = w.mActivityRecord; if (focusedApp == null ) { ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_FOCUS_LIGHT, "findFocusedWindow: focusedApp=null using new focus @ %s" , w); mTmpWindow = w; return true ; } if (!focusedApp.windowsAreFocusable()) { ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_FOCUS_LIGHT, "findFocusedWindow: focusedApp windows not" + " focusable using new focus @ %s" , w); mTmpWindow = w; return true ; } if (activity != null && w.mAttrs.type != TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING) { if (focusedApp.compareTo(activity) > 0 ) { ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_FOCUS_LIGHT, "findFocusedWindow: Reached focused app=%s" , focusedApp); mTmpWindow = null ; return true ; } } ProtoLog.v(WM_DEBUG_FOCUS_LIGHT, "findFocusedWindow: Found new focus @ %s" , w); mTmpWindow = w; return true ; };
更新焦点窗口的步骤也不复杂:
遍历该DisplayContent中mChildren中的所有DisplayArea
依次对比DisplayArea中的mChildren集合里面的Window(ActivityRecord或WindowState)
检查该Window是否符合要求
无法接收输入事件的窗口没有资格作为焦点窗口
如果当前没有焦点窗口,那么遍历的第一个可接受input事件的窗口就是焦点窗口了
如果当前焦点窗口已经不在可聚焦了,那么也是遍历的第一个可接受input事件的窗口作为焦点窗口
遍历所有app的token, 找到第一个符合要求的作为焦点窗口
WindowState对应的有Activity, 而且类型不能是启动窗口
该Activity窗口Z轴比当前焦点窗口大
更新mTmpWindow为当前Activity窗口,否则置为null
1.6 ActivityRecord.compareTo ActivityRecord其实是调用了父类WindowContainer中的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 @Override public int compareTo (WindowContainer other) { if (this == other) { return 0 ; } if (mParent != null && mParent == other.mParent) { final WindowList<WindowContainer> list = mParent.mChildren; return list.indexOf(this ) > list.indexOf(other) ? 1 : -1 ; } final LinkedList<WindowContainer> thisParentChain = mTmpChain1; final LinkedList<WindowContainer> otherParentChain = mTmpChain2; try { getParents(thisParentChain); other.getParents(otherParentChain); WindowContainer commonAncestor = null ; WindowContainer thisTop = thisParentChain.peekLast(); WindowContainer otherTop = otherParentChain.peekLast(); while (thisTop != null && otherTop != null && thisTop == otherTop) { commonAncestor = thisParentChain.removeLast(); otherParentChain.removeLast(); thisTop = thisParentChain.peekLast(); otherTop = otherParentChain.peekLast(); } ...... if (commonAncestor == this ) { return -1 ; } else if (commonAncestor == other) { return 1 ; } final WindowList<WindowContainer> list = commonAncestor.mChildren; return list.indexOf(thisParentChain.peekLast()) > list.indexOf(otherParentChain.peekLast()) ? 1 : -1 ; } finally { mTmpChain1.clear(); mTmpChain2.clear(); } }
可以将WC的整个结构理解为树形结构,对比两个WC的Z轴大小就是对比这两个WC与最近的共同父节点的距离大小,距离越大,说明Z轴越大。
1.6.1 WindowContainer.getParents 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 private void getParents (LinkedList<WindowContainer> parents) { parents.clear(); WindowContainer current = this ; do { parents.addLast(current); current = current.mParent; } while (current != null ); }
依次遍历,将该WindowContainer的所有mParent添加到队列中.
二. 小结 总的来说,更新焦点窗口就是对所有DisplayContent倒序遍历,依次计算新的焦点窗口:
计算当前DisplayContent的焦点窗口
遍历该DisplayContent中mChildren中的所有DisplayArea
依次对比DisplayArea中的mChildren集合里面的Window(ActivityRecord或WindowState)
检查该Window是否符合要求
无法接收输入事件的窗口没有资格作为焦点窗口
如果当前没有焦点窗口,那么遍历的第一个可接受input事件的窗口就是焦点窗口了
如果当前焦点窗口已经不在可聚焦了,那么也是遍历的第一个可接受input事件的窗口作为焦点窗口
遍历所有app的token, 找到第一个符合要求的作为焦点窗口
WindowState对应的有Activity, 而且类型不能是启动窗口
该Activity窗口Z轴比当前焦点窗口大
更新mTmpWindow为当前Activity窗口,否则置为null
如果计算的新焦点窗口和当前焦点窗口是同一个,则无需额外动作
如果当前存在输入法窗口,执行相关操作(后续分析输入法窗口)
更新焦点窗口,保存在mCurrentFocus中
清空mWinAddedSinceNullFocus、mWinRemovedSinceNullFocus
通知其他模组焦点窗口更新了,主要是更新两个Task(当前焦点窗口和新的焦点窗口所处的Task)的阴影
更新DisplayPolicy中相关参数
更新DisplayFoldController中的mFocusedApp(焦点窗口包名),然后根据需要更新SystemUI的可见性
如果因焦点窗口变化导致SystemUI状态栏或者导航栏可见性有变化了,将参数mLayoutNeeded置位true
将没有焦点的窗口的toast在超时时间后移除,防止其覆盖UI
记录新焦点窗口,保存在mLastFocus中
在WMS计算更新完焦点窗口之后,需要同步通知给input系统:
1 2 3 4 5 if (focusChanged) { displayContent.getInputMonitor().setInputFocusLw(displayContent.mCurrentFocus, false ); }
这里很自然就有疑问,窗口可大可小,不同的窗口层叠起来,input系统是如何判断分发事件到正确的窗口呢? 接下来我们先看看应用窗口和input的关系。